Research Interests:
- AAV viral vector optimization for targeted gene delivery
- Development of viral strategies for neurological therapeutics
- Gene therapy drug delivery systems for complex disease models
Main Research: Graphical Abstracts
We describe and validate three small pan-neuronal promoters isolated from the genome of the alphaherpesvirus, using neuron primary cells culture and mouse model. Promoters drive efficient and long-term transgene expression in the central nervous system after single-dose administration. For more details, check out our paper.
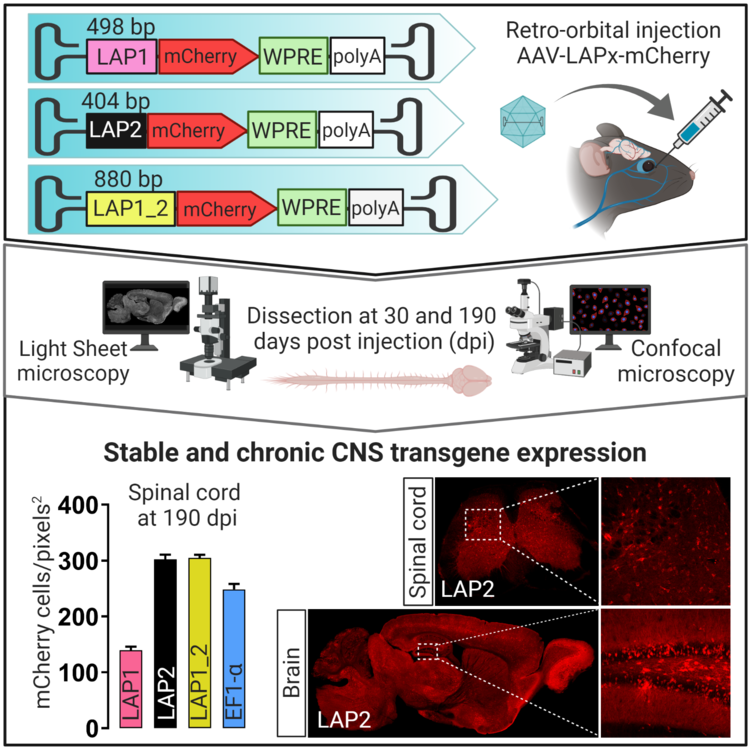
We validated a short (404 bp), strong and persistent promoter obtained from the genome of pseudorabies virus (PRV) called alphaherpesvirus latency-associated promoter 2 (LAP2) in peripheral tissue. We demonstrate that different cell types can efficiently express a transgene when transduced by AAV8-LAP2 or AAV9-LAP2 following local or systemic administration. Here is our new article published on Journal Virological Methods.

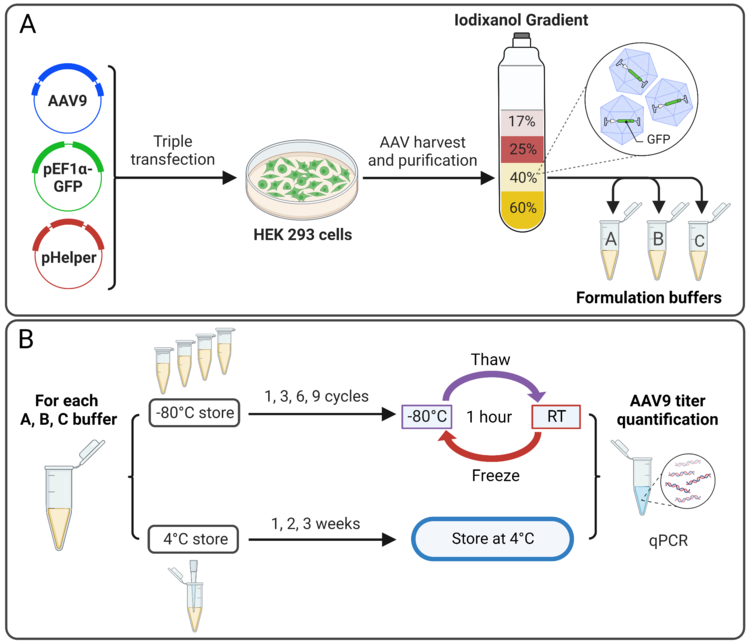
We developed an assay for single-cell quantification of incoming AAV genome in neurons through a mathematical model using neuron primary cells culture and mouse model. Methodology and results can be found in our paper.
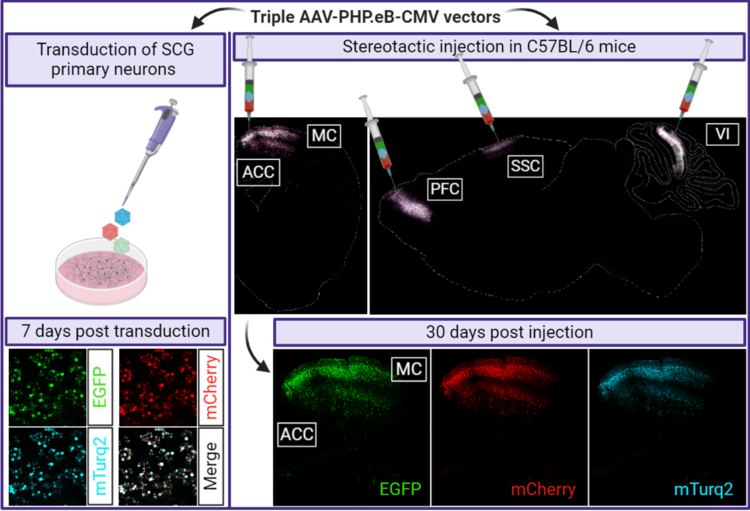
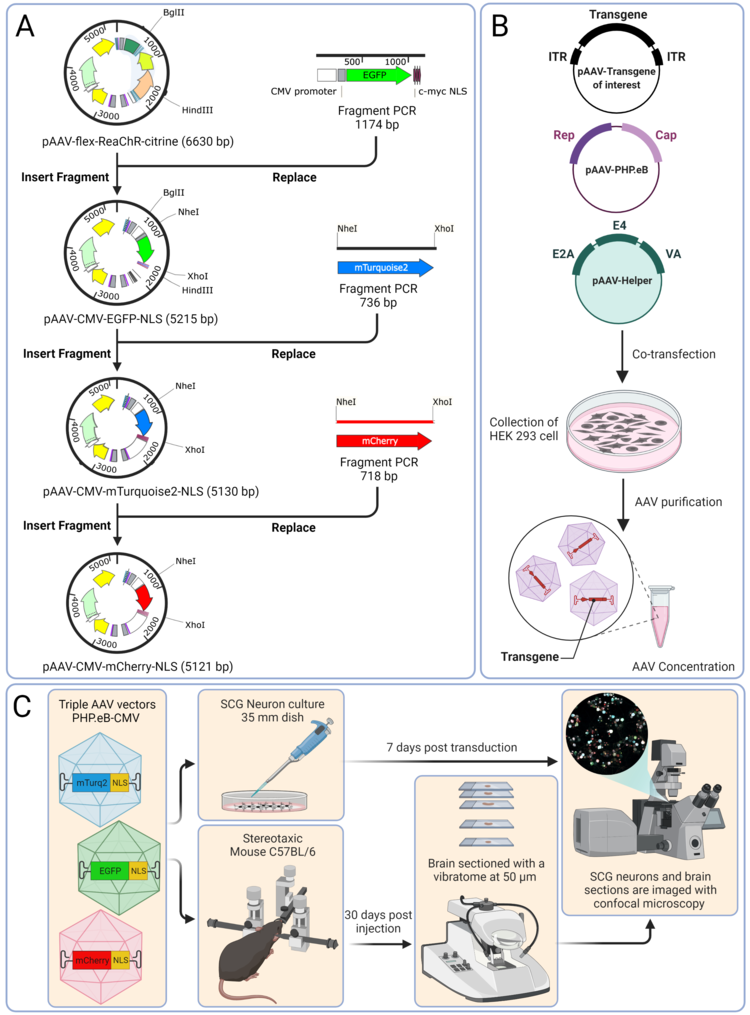
We design a protocol for A) construction of triple-AAV plasmid, B) production of AAV vectors, C) triple-AAV transduction of primary superior cervical ganglia (SCG) neuronal cultures, mouse surgery and triple-AAV injection, image analysis and AAV genome quantification with single-cell resolution. Chek out our paper.
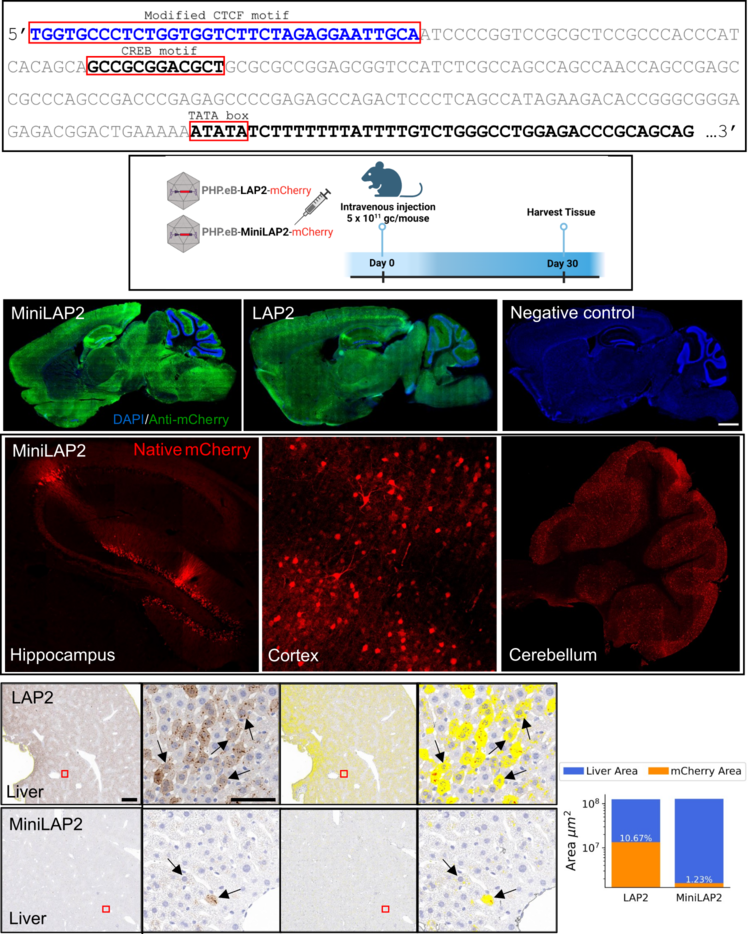
We Introduced MiniLAP2, a compact neural promoter enabling precise transgene expression in brain. Minimal off-target effects observed in peripheral tissues. Promising potential for safe and effective therapeutic delivery by AAV vector. Here is our new article published on Gene Therapy
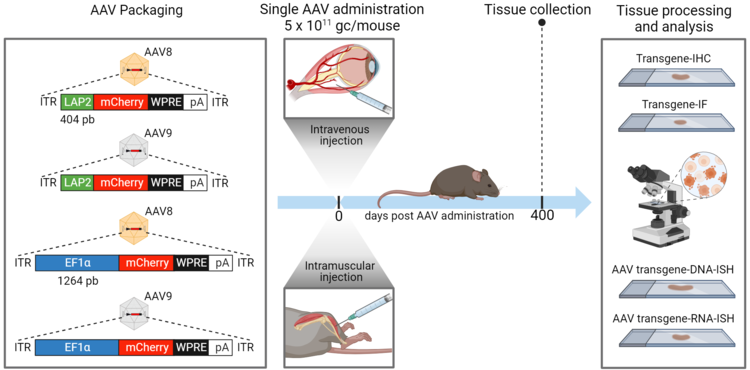
We assessed the efficacy of LAP2, a compact promoter derived from pseudorabies virus, for driving transgene expression compared to the conventional EF1α promoter in mice after one year (400 days) post administration. Injecting LAP2 and EF1α packaged into AAV8 and AAV9 vectors, we observed robust transgene expression in liver, kidney, and skeletal muscle, suggesting LAP2's potential for gene therapy applications requiring efficient delivery of large or multiple therapeutic genes for long-term. Here is our latest article published in Frontier in Virology